Different types of keloids
Hypertrophic Scars
An important differential diagnosis is hypertrophic scar. This will project maximum 4 millimetres above surrounding skin. As a rule, it will never extend beyond the initial area of injury, while, keloids will always extend beyond the area of original trauma. Keloid had whorl of hyalinised collagen without blood capillaries while hypertrophic scar will have regularly arranged parallel collagen and intact vertical capillaries in between.
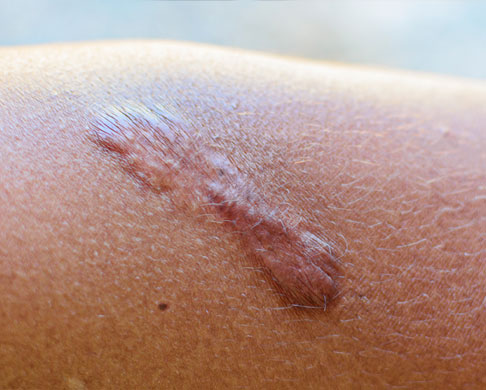
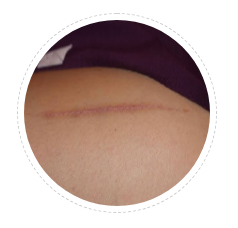
Linear Keloid
Keloid showing in a line has to be differentiated from linear hypertrophic scars. Keloid has one or more active borders. These lines usually follow pressure transmission lines.
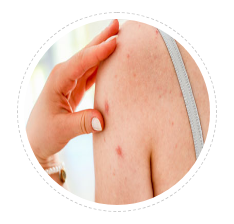
Papular Keloid
This is the smallest form of keloid. Usually comes after a acne of hair follicular infection. All big lesions small papule only.
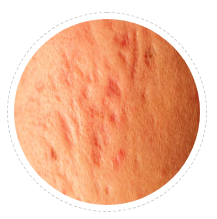
Post acne Keloid
Keloid after acne or chicken pox are common in predispose individuals. They start as popular keloids and soon become linear by joining two or more together.
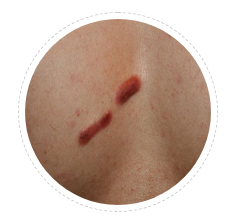
Chest / Sternal Keloid
Chest is one of the peculiar and most common sites for kelid formation. Rich appendages and tension makes it prone for keloids. Hair follicle infection and acne are common trigger factors.
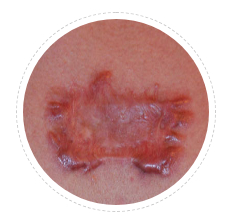
Butterfly Keloid
This is common on chest. It has a narrow but thick center while multiple lines of spread at periphery. These lines represent pressure transmission lines. This looks like butterfly. Many a times we need to restrict chest movements like exercise while chest keloid is active. In females, they are advised to wear supportive bras to reduce tension in keloid area.
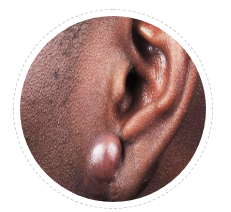
Massive Keloid
Although massive keloids are common in African skin of color. Many Indian patients develop massive keloids. They often have family history of severe keloid and repeated surgery.
Superficial Spreading
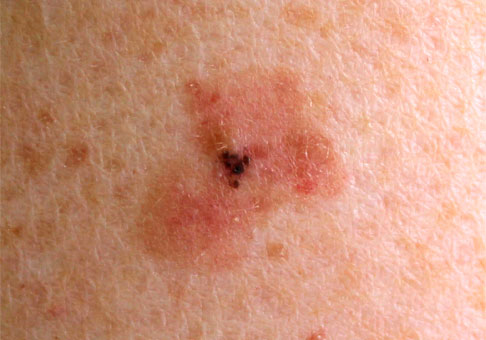

Post Surgical
In genetically predisposed individuals, surgery scar can leave a keloid behind. Slowly healed wound, low grade wound infection, hair follicles trapped in sutures are few common predisposing features. Inflammatory sutures used in subcutaneous suturing is yet another cause.
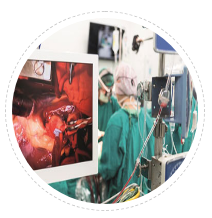
Post Cardiac Surgery
In CABG surgery chest wound is vulnerable to keloids. Here bony chest wall is cut and sutured with stainless still wires. Each breath creates movement. This movement makes this area prone for keloid. In a study two patients in every 10 patients undergone sternotomy during CABG had symptomatic scar (22%) while one in every ten (10%) had hypertrophic scar in mid chest.
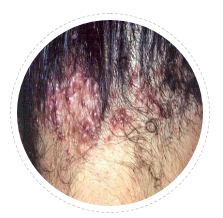
AKN Acne keloidalis nuchae
This is a peculiar condition where acne like lesions in posterior scalp develop popular keloids which can grow massive nodular keloid. Hair follicle involvement and recurrent infections are trigger for growth. Treating this hairy area is a therapeutic challenge.
